Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Tunable Laser Technology, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Key Laboratory of Micro-Nano Optoelectronic Information System, Shenzhen Graduate School, Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
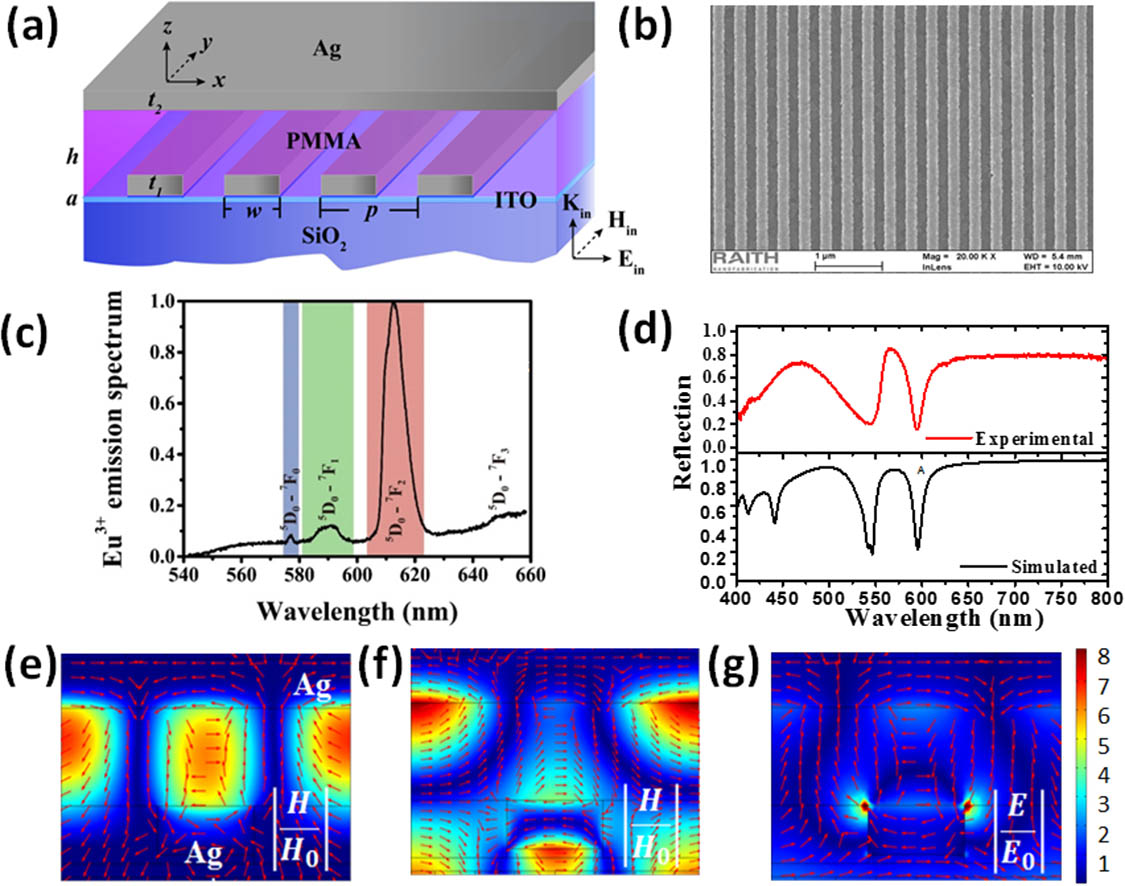
Magnetic dipole (MD) transitions are important for a range of technologies from quantum light sources and displays to lasers and bio-probes. However, the typical MD transitions are much weaker than their electric counterparts and are usually neglected in practical applications. Herein, we experimentally demonstrate that the MD transitions can be significantly enhanced by the well-developed magnetic metamaterials in the visible optical range. The magnetic metamaterials consist of silver nanostrips and a thick silver film, which are separated with an Eu3+:polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) film. By controlling the thickness of the Eu3+:PMMA film, the magnetic resonance has been tuned to match the emission wavelength of MDs. Consequently, the intensity of MD emission has been significantly increased by around 30 times at the magnetic resonance wavelength, whereas the intensity of electric dipole emission is well-preserved. The corresponding numerical calculations reveal that the enhancement is directly generated by the magnetic resonance, which strongly increases the magnetic local density of states around the MD emitter and can efficiently radiate the MD emission into the far field. This is the first demonstration, to the best of our knowledge, that MD transitions can be improved by an additional degree of magnetic freedom, and we believe this research shall pave a new route towards bright magnetic emitters and their potential applications.
160.3918 Metamaterials 160.6990 Transition-metal-doped materials 350.5400 Plasmas 310.6628 Subwavelength structures,nanostructures 300.6550 Spectroscopy, visible Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 050008
1 吉林大学 超硬材料国家重点实验室, 吉林 长春130012
2 吉林大学 物理学院, 吉林 长春130012
引用一种带有量纲的电子-声子相互作用常数, 很容易建立它与黄昆因子的关系式, 进而计算出类胡萝卜素分子每个碳碳振动模的电子-声子耦合常数。测量了β胡萝卜素分子在极性溶剂1, 2-二氯乙烷和非极性溶剂环己烷中20~60 ℃的温度范围内紫外-可见吸收光谱和共振拉曼光谱。结果表明, 在极性溶剂1, 2-二氯乙烷中,β胡萝卜素分子的碳碳键拉曼散射截面小,黄昆因子、电子-声子耦合数比非极性溶剂中大。为了解释这种现象, 我们引入线性多烯分子的两种模型, 即F A C Oliveria引入的有效共轭长度模型和D Yu Paraschuk提出的相干弱阻尼电子-晶格振动模型。
黄昆因子 电子-声子耦合系数 线性多烯 Huang-Ryes factor electron-phonon coupling constant linear polyenes
1 吉林大学超硬材料国家重点实验室, 物理学院, 吉林 长春130012
2 吉林大学第二医院, 吉林 长春130041
β-胡萝卜素具有光采集、 光防护功能, 又是重要的光电材料, 它在外场下的分子结构和性能变化既有理论意义也有应用价值。 测量了β-胡萝卜素在环己醇中68~26 ℃温度范围内的紫外-可见吸收、 拉曼光谱。 实验结果表明随着温度的降低, 黄琨因子和碳碳键每个振动模的电子-声子耦合常数减小, 紫外-可见吸收光谱红移, 碳碳键拉曼散射截面增加。 用线性链状多烯分子的“相干弱阻尼电子-晶格振动模型”、 “有效共轭长度模型”等理论给予了解释。 随着温度的降低, β-胡萝卜素分子的热无序减小, 分子结构有序性增加, π电子离域扩展, 有效共轭长度增加, 导致紫外-可见吸收光谱红移和强的拉曼活性。 相干弱阻尼电子-晶格振动增强, 使碳碳键拉曼散射截面增加。 引用带有量纲的电子-声子相互作用常数, 既可以与黄昆因子建立关系式, 计算出碳碳键每个振动模的数值, 也可以表征分子的有效共轭长度, π电子离域程度及拉曼散射截面的大小等。
β-胡萝卜素 黄琨因子 电子-声子耦合常数 All-trans-β-carotene Huang-Ryes factor Electron-phonon coupling constant 光谱学与光谱分析
2013, 33(9): 2311
1 吉林大学 物理学院, 吉林 长春 130012
2 青岛理工大学 理学院, 山东 青岛 266033
测量了四氯化碳在苯中不同浓度的拉曼光谱, 分析了不同浓度下四氯化碳v1+v4~v3费米共振的变化。结果表明:随着浓度的降低, 两费米双光谱强度比R增加, 而频差Δ减小、费米共振耦合系数W减小、非谐力常数K增加。这种费米共振随浓度的变化是由溶剂效应引起的, 即随着四氯化碳在苯中的浓度降低, 其拉曼散射系数(光谱强度)增加, 使两费米双线光谱强度增加而减弱了费米共振。
费米共振 拉曼光谱 溶剂效应 Fermi resonance Raman spectroscopy solvent effect





